Stepper motors
A stepper motor is designed to provide a particularly high level of positional precision by moving only in discrete steps. Control is achieved using multiple pairs of electromagnetic poles and toothed cores which align in a particular way when the magnets are energised. Stepper motors are a good choice for applications that are sensitive to position, such as 3D printing, camera control, etc. However, the improved precision is gained at the expense of lower efficiency and lower torque. Figure 4 illustrates the operation of a four-pole stepper. Notice that to achieve maximum performance from the stepper, each electromagnet requires its own control signal. The more poles, the more control signals are needed. Because some of the connections always have opposite polarity, it is possible to achieve some reductions in the number of control connections, and this is discussed in the second link in the resources box.
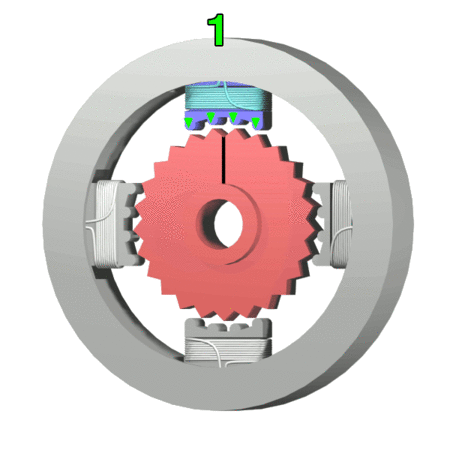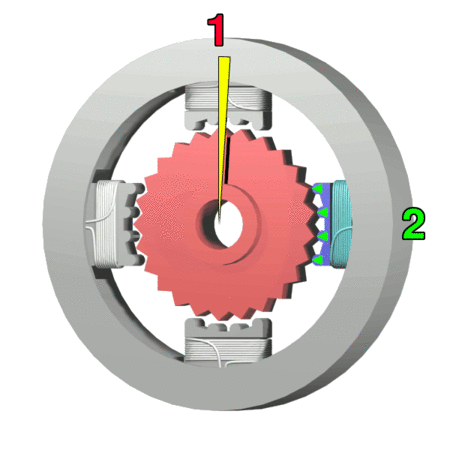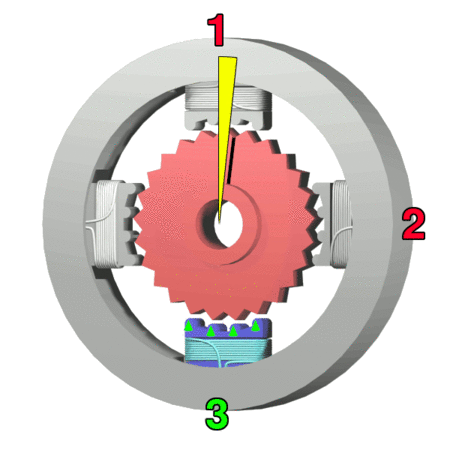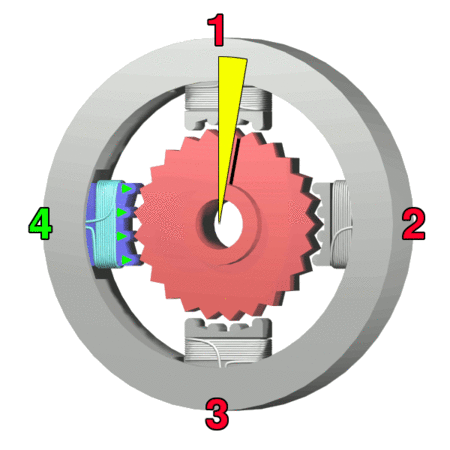
Figure 4: Operation of a four-pole stepper motor
by Wapcaplet; Teravolt. The original uploader was Teravolt at
English Wikipedia GFDL, via
Wikimedia Commons